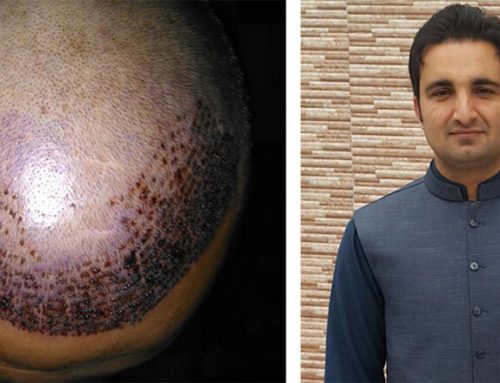
We are familiar with typical male baldness of hereditary origin, being the most frequent, but also there are alopecias generated by infectious processes. Contagion occurs through hats, combs or clothing of other affected persons and, in the case of the most common, ringworm or dermatophytosis, also by contact with infected cats and other pets.
Ringworm is due to the action of dermatophyte fungi , which need a warm and moist environment to grow. Excessive sweating, poor hygiene, and small lesions on the scalp make development more likely. This fungal disease occurs most frequently in childhood and usually disappears at puberty. It causes pruritus and hair loss in infected areas; The skin may peel and show inflammation or redness and even ulceration. Occasionally, it is accompanied by fever or lymph node inflammation.
Infections That Causes Hair Loss:
Other diseases of infectious origin that can lead to hair loss are due to the action of viruses . For example, herpes or chickenpox can affect the scalp and cause alopecia temporarily or, if scraping injuries occur, lead to permanent alopecia localized to the scars of these lesions.
As for bacterial infections related to hair loss, necrotic acne, leprosy and syphilis are the diseases that most often cause cases of alopecia. Also elephantiasis, due to the action of protozoa , or folliculitis decalvante, an inflammatory process in hair transplant in Islamabad lead to hair cure.
The effective solution in these infectious processes requires the intervention of the medical professional. An assessment of the specialist is crucial to obtain a correct diagnosis and propose the most appropriate treatment to the origin of the disease. There are specific medicines for each of these alterations and hygiene measures that must be taken by the patient and his environment, without which it is not possible to eradicate the germs involved.